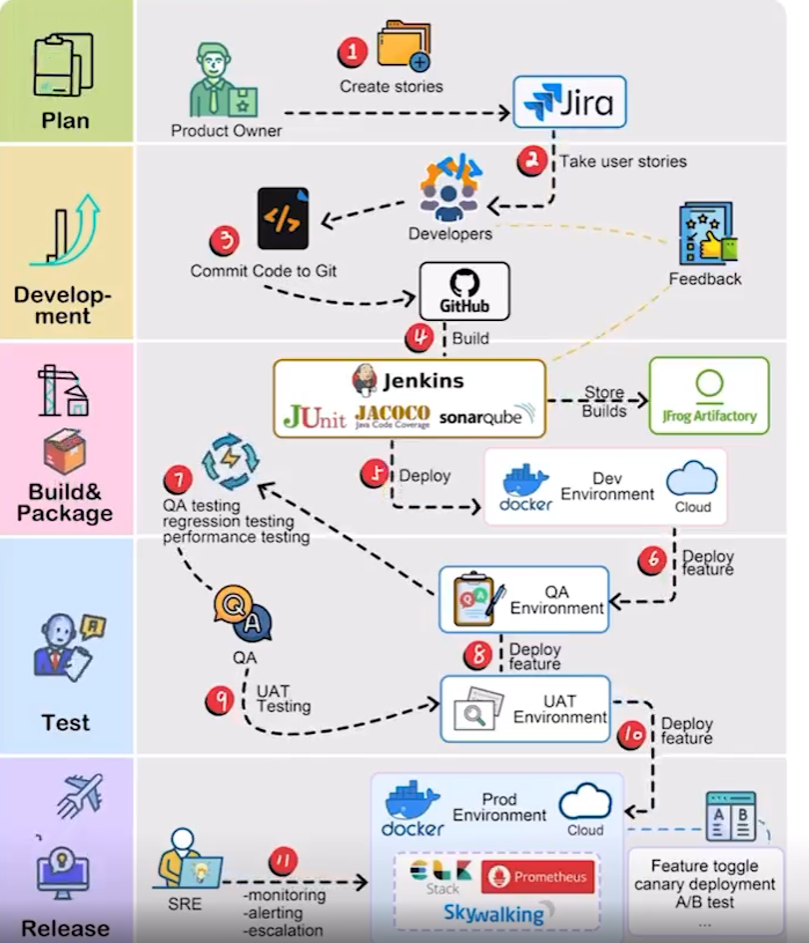
Curious about how code makes its way to production? Here’s a glimpse into the typical workflow:1. Product Vision: The process begins with the product owner crafting user stories based on requirements.2. Sprint Development: The development team selects these user stories from the backlog and incorporates them into a sprint for a two-week development cycle.3. Code Commit: Developers commit their code to the Git repository.4. Build Automation: Jenkins triggers a build, which must pass unit tests, code coverage thresholds, and quality gates in SonarQube.5. Artifact Management: Upon a successful build, the artifact is stored in Artifactory and deployed to the development environment.6. Feature Testing: With multiple dev teams working on various features, each feature is deployed to QA1 and QA2 for independent testing.7. QA Assurance: The QA team performs QA testing, regression testing, and performance testing on the new environments.
8. UAT Deployment: Following successful QA testing, the builds are deployed to the UAT environment.
9. Release Candidate: If UAT is successful, the builds are marked as release candidates and scheduled for deployment to the production environment.10. Production Monitoring: The SRE (Site Reliability Engineering) team takes charge of monitoring the production environment.